LruCache的基本使用
在使用LruCache时,一般需要重写sizeOf方法,该方法用于返回一个对象所占用的内存大小
//获取系统分配给每个应用程序的最大内存
int maxMemory=(int)(Runtime.getRuntime().maxMemory()/1024);
int cacheSize=maxMemory/8;
private LruCache<String, Bitmap> mMemoryCache;
//给LruCache分配1/8
mMemoryCache = new LruCache<String, Bitmap>(mCacheSize){
//重写该方法,来测量Bitmap的大小
@Override
protected int sizeOf(String key, Bitmap value) {
return value.getRowBytes() * value.getHeight()/1024;
}
};LruCache的构造函数
public LruCache(int maxSize) {
if (maxSize <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("maxSize <= 0");
}
this.maxSize = maxSize;
this.map = new LinkedHashMap<K, V>(0, 0.75f, true);
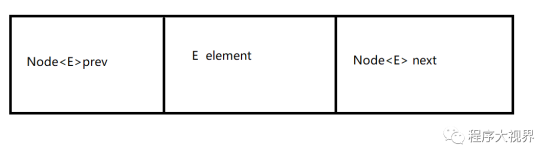
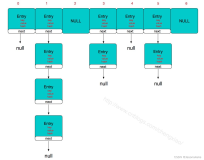
}可以看到c的本质是维护了一个LinkedHashMap,我们看下LinkedHashMap的构造函数的第三个参数的含义
/**
* Constructs an empty <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt> instance with the
* specified initial capacity, load factor and ordering mode.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity 初始化大小
* @param loadFactor the load factor 加载因子
* @param accessOrder the ordering mode - <tt>true</tt> for
* access-order, <tt>false</tt> for insertion-order
* //如果是true代表是访问顺序,如果是false代表插入顺序
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative
* or the load factor is nonpositive
*/
public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity,
float loadFactor,
boolean accessOrder) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
this.accessOrder = accessOrder;
}LruCache是通过维护一个根据访问顺序排序的LinkedHashMap
put方法
public final V put(K key, V value) {
// 参数合法性检查
if (key == null || value == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key == null || value == null");
}
V previous;
synchronized (this) {
putCount++;
//safeSizeOf调用是sizeOf,需要我们重写,用于计算对象的大小
size += safeSizeOf(key, value);//总的大小加上新的
previous = map.put(key, value);//调用LindedHashMap的put,向map中加入缓存对象,若对象已存在,返回已有的值,如果不存在则返回null
if (previous != null) {
size -= safeSizeOf(key, previous);//如果对象已经存在,需要减掉上一个的
}
}
// entryRemoved默认是空实现,我们根据需要自行实现,用于对象删除之后的操作
if (previous != null) {
entryRemoved(false, key, previous, value);
}
// 调整缓存的大小
trimToSize(maxSize);
return previous;
}put方法主要是调用LindedHashMap的put来保存数据,调整缓存大小。并调用trimToSize来判断缓存是否已经满了,如果大于了最大的缓存大小,通过循环不断删除最近最少使用的对象,直到缓存大小小于最大的缓存大小
trimToSize方法
public void trimToSize(int maxSize) {
while (true) {
K key;
V value;
synchronized (this) {
// 如果缓存小于0或者map为空而缓存大小不为0,抛出异常
if (size < 0 || (map.isEmpty() && size != 0)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(getClass().getName()
+ ".sizeOf() is reporting inconsistent results!");
}
//没有超过最大的缓存大小,不需要做任何操作,直接跳出循环
if (size <= maxSize) {
break;
}
//从缓存map中找到最近最少使用的对象,如果不存在直接跳出循环
Map.Entry<K, V> toEvict = map.eldest();
if (toEvict == null) {
break;
}
key = toEvict.getKey();
value = toEvict.getValue();
map.remove(key);//map中删除这个对象
size -= safeSizeOf(key, value);//调整目前缓存大小
evictionCount++;//回收次数+1
}
//默认空实现
entryRemoved(true, key, value, null);
}
}trimToSize主要维护缓存size的大小,确保缓存小于最大的缓存值。一旦发现大于最大缓存值,调用map的eldest方法找到最近最少使用的对象,并删除。eldest是获取LinkedHashMap的队首的元素。
get方法
public final V get(K key) {
if (key == null) {// 参数合法性检查
throw new NullPointerException("key == null");
}
V mapValue;
synchronized (this) {
mapValue = map.get(key);//根据key的到对象的value
//如果对象存在,则返回这个value
if (mapValue != null) {
hitCount++;//命中数+1
return mapValue;
}
missCount++;
}
/*
* Attempt to create a value. This may take a long time, and the map
* may be different when create() returns. If a conflicting value was
* added to the map while create() was working, we leave that value in
* the map and release the created value.
* 如果通过key从缓存集合中获取不到缓存数据,则尝试使用creat方法创造一个value。
* create默认实现是返回null,需要的时候可以重写这个方法
*/
V createdValue = create(key);
if (createdValue == null) {
return null;
}
// 如果创建成功,则将新的value添加到map中,跟put方法类似
synchronized (this) {
createCount++;
mapValue = map.put(key, createdValue);
if (mapValue != null) {
// There was a conflict so undo that last put
map.put(key, mapValue);
} else {
size += safeSizeOf(key, createdValue);
}
}
if (mapValue != null) {
entryRemoved(false, key, createdValue, mapValue);
return mapValue;
} else {
trimToSize(maxSize);
return createdValue;
}LruCache的get方法,从集合中获取缓存,本质是调用LinkedHashMap的get,每调用一次get就代表访问了一次该元素,将会更新队列,保持整个队列是按照访问顺序排序。下面是LinkedHashMap的get的实现
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null)
return null;
if (accessOrder)
afterNodeAccess(e);//将e移到队尾,保证按照访问顺序排序
return e.value;
}总结
LruCache中维护了一个集合LinkedHashMap,LinkedHashMap是以访问顺序排序的。
主要的核心方法put、get和trimToSize。put和get是调用LinkedHashMap的put和get。通过trimToSize确保缓存小于最大缓存值。